Its Components
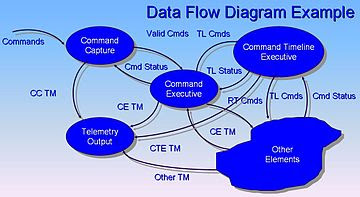
 These diagrams consist of many components in helping making organized, structured systems of information input and output. The first component is external entities or what is called terminators. External entities identify the destination and sources of information including the flow of information, both input and output. An external entity can be a person, an object, or an organization that has a pre-defined character or behavior. Flows are also one of the most important components. From its name, flows define the interactions between entities and the components. It as well connects and defines interactions between inside and outside sources. There are several types of data flows which include: Bi-Directional data flows, Data flows with the same name, Complex data flows, and trivial data flows. Bi-Directional data flow only shows identical information that flow in the same direction. Data flows with the same name are all identical. Multiple of these data flows will be used in the same way. Complex data flow happens when there is more than one data flowing in the same direction between two entities. Data flows don’t contain trivial flows where error messages will be shown. Keys to retrieve data flows and information are also absent in the DFD and the system. Stores are one of the factors needed in a data flow diagram. Stores represent information at rest, in use at times and processes only when information needs to presented. Stores often have different time periods to become active and active. Information, therefore, can be written in a store and also read from a store. Generally, a store is information that can be use at different times due to its flexibility and the ability to be both active and inactive. Data stores are stores created for later use. To simplify shortly, data stores are stores that are temporarily inactive. Processes are functionality of systems. It transforms and changes input information such as stores or data into output information. Control processes are used to transform input data into output data. Data processes, on the other hand, turn input information to output information.
These diagrams consist of many components in helping making organized, structured systems of information input and output. The first component is external entities or what is called terminators. External entities identify the destination and sources of information including the flow of information, both input and output. An external entity can be a person, an object, or an organization that has a pre-defined character or behavior. Flows are also one of the most important components. From its name, flows define the interactions between entities and the components. It as well connects and defines interactions between inside and outside sources. There are several types of data flows which include: Bi-Directional data flows, Data flows with the same name, Complex data flows, and trivial data flows. Bi-Directional data flow only shows identical information that flow in the same direction. Data flows with the same name are all identical. Multiple of these data flows will be used in the same way. Complex data flow happens when there is more than one data flowing in the same direction between two entities. Data flows don’t contain trivial flows where error messages will be shown. Keys to retrieve data flows and information are also absent in the DFD and the system. Stores are one of the factors needed in a data flow diagram. Stores represent information at rest, in use at times and processes only when information needs to presented. Stores often have different time periods to become active and active. Information, therefore, can be written in a store and also read from a store. Generally, a store is information that can be use at different times due to its flexibility and the ability to be both active and inactive. Data stores are stores created for later use. To simplify shortly, data stores are stores that are temporarily inactive. Processes are functionality of systems. It transforms and changes input information such as stores or data into output information. Control processes are used to transform input data into output data. Data processes, on the other hand, turn input information to output information.How to draw a dataflow diagram
Drawing DFDs are indeed simple and useful for all businesses. The system itself will enhance productivity and save time due to its organized structure and system which involves the use of figures, symbols, and shapes to represent information flow, input information, output information and many other processes that will further make the development of tasks and the distribution of work easy and well organized. First of all, knowing the symbols is a must. Without knowing about what each symbol means, working on a data flow diagram will be impossible. According to Gane and Sarson, round edged rectangles symbolize processes that take place in a data flow diagram. Squares represent external entities; arrows indicate flows of information, both output and input; open ended rectangles identify stores. A diagonal line below a square indicates that this data is present elsewhere but in the same data flow diagram. An extra diagonal line on a rectangle also indicates that it appears somewhere in the same data flow diagram. Pursuant to Yourdon and Demarco, circles represent processes, squares are external entities, and arrows show the flow of information. Lastly, rectangles open on both ends represent stores. To decide on a right notation, it greatly depends on the real-time events and situations. These notations are extended to expand the uses of these symbols so things will be well-organized when it comes to real situations and working times. The widely adopted convention is to add dashed lines in order to represent the control components. Dashed lines are accepted in both notations.
Its importance in business
The importances of data flow diagrams are vast. DFDs help businesses build up their confidentiality in making safe decisions. The processes, monitoring of input and output information will help them plan further ahead. Data flow diagrams help in presentations; presentations are often one of the most challenging tasks business men and women would have to face. With data flow diagrams and its simple representations through symbols and figures, presenting will no longer be a difficult task. Error detection is also one of the serious problems businesses face. Keeping track of errors is not an easy job. However, with data flow diagrams, programmers can point out errors easily.